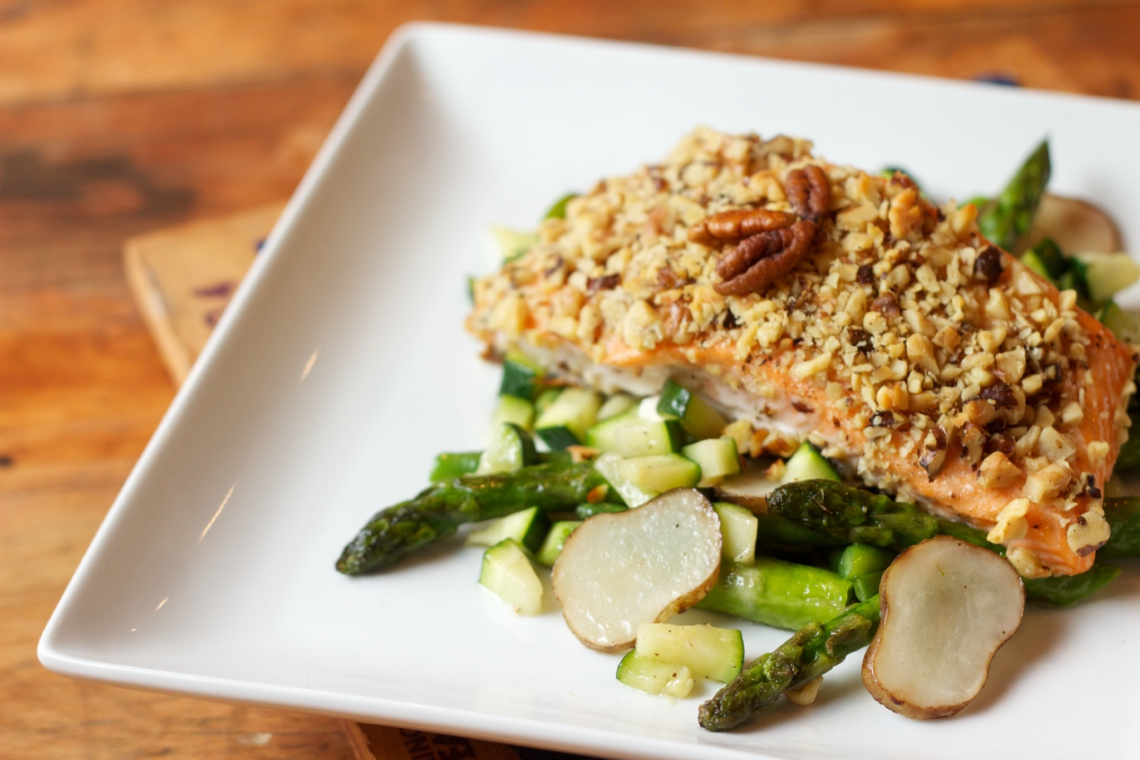

Are you eating balanced meals?
Recently, I read a post about balanced meals on Instagram. The post compared how your body feels when you are eating balanced meals and when you are not. Although this is not a scientific way to evaluate your food choices, it may indicate an issue in your current diet. Read each column and see which one sounds like you.
Balanced
- satisfied after eating
- generally more energetic and happy after eating
Unbalanced
- hangry in-between meals
- sluggish, sad or anxious after eating
- have cravings after eating despite being full
Based on this criteria, I realized that I am making good food choices since I experience more signs from the first column. Before I became knowledgeable about making good food choices, I felt more like the second column. I was always hungry and tended to snack on sugary foods, particularly after lunch.
When I started making better choices, I felt better physically and mentally. Here are some examples of how I gradually improved my eating habits. Physically, I was more energetic throughout the day and made more progress in the gym. Mentally, I felt more coherent, which improved my productivity.
Is your current diet fueling you properly? If you are feeling great after eating, continue your current habits. If you are frequently feeling hangry or having cravings after meals may indicate that you need to make some changes to your current diet. Either way, continue reading to learn about balanced meals and how to create them.
What is a balanced meal?
In general, a balanced diet “gives your body the nutrients it needs to function correctly (healthline.com). These vital nutrients come from macronutrients (macros for short), which are carbohydrates, protein, and fat. Since these nutrients support different bodily processes and functions, it is important to include foods from each category in your diet.
If you are eating balanced meals, you will receive these components throughout the day. A table listing more information about each macronutrient is listed below.
| Macronutrient | Function | Examples |
| Carbohydrate | -provides energy to the body -maintains blood sugar | bread, pasta, oatmeal, fruit, vegetables, quinoa |
| Fat | – stores energy -absorption and transportation of fat-soluble vitamins. -protects and insulates vital organs. | nuts and seeds, oils, nut butter |
| Protein | – aids muscle growth and repair – essential for body tissue development, maintenance and repair | eggs, dairy products, meat, poultry, fish |
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) recommends that meals should contain foods from the following five food groups: fruits, vegetables, grains, protein and dairy. Here is the daily recommended servings for each food group for sedentary adults:
- Fruits: 2 cups
- Vegetables: 2.5-3 cups
- Grains: 6-8 ounces (3 ounces minimum)
- Protein: 5-6 ounces
- Dairy: 3 cups
Ideally, all of our meals should resemble the diagram below in order to create balanced meals throughout the day.

However, your meals may vary from this diagram based on your activity level, medical conditions and additional factors.
How do I create balanced meals?
Essentially, each meal should contain a carb, fat, and protein. If you are a vegetarian or vegan, you must make sure you are eating complete protein sources or combining incomplete proteins. However, not all foods are created equal. Try to prioritize nutrient-dense foods, or foods low in calories but high in nutrients, in your meals for maximum benefits. An example is eating oatmeal instead of cereal for breakfast. If you have a busy schedule, consider meal prepping and choosing healthy pre-packaged snacks to help you stay on track.
Sometimes, we want to indulge in our less healthy favorite foods without the after effects. Here is a recent example of how I incorporated homemade pizza into my lunch.
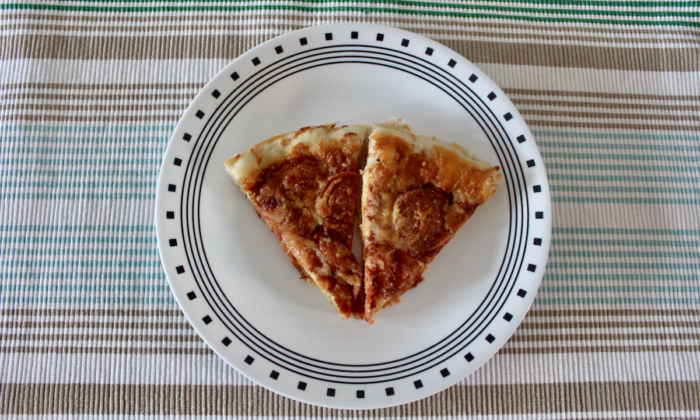
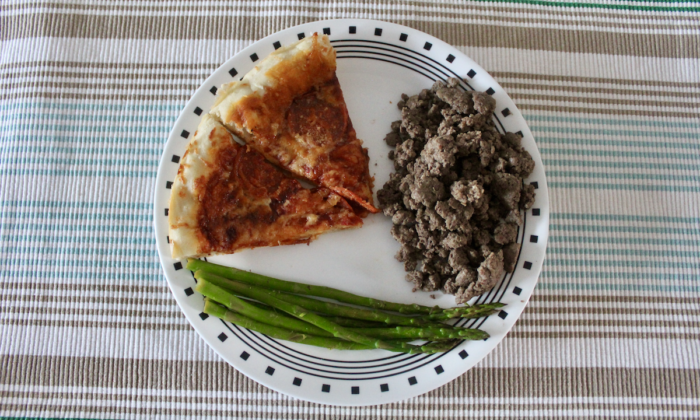


Initially, the pizza would have provided me with carbs and fat, but was lacking protein. The addition of lean ground beef and asparagus provided satiety and nutrients that were not included before.
Not sure where to start? Check out my suggestions and create meals by using the chart below.
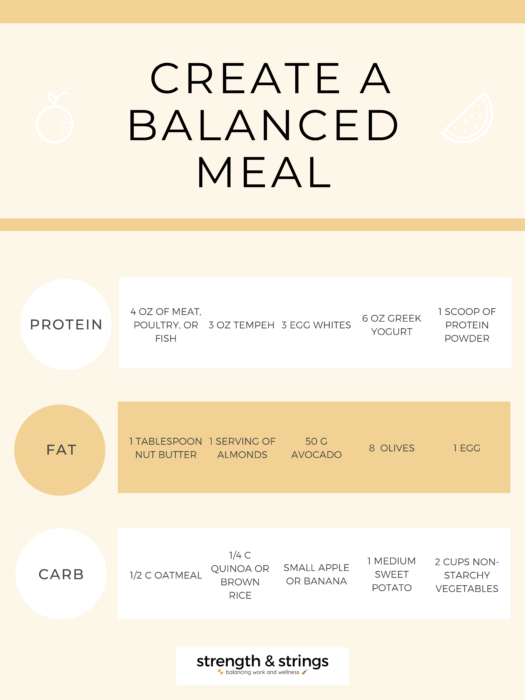
Final considerations
Eating balanced meals is essential for a healthy and productive life. If you are unsure about your current diet, please consult a medical professional, registered dietitian (RD), or nutritionist.






